Summary of Electrical Substations and benefits of using Dust Sensors
What is an electrical substation?
A substation is a facility to control electricity power and it transforms voltage from high to low or the reverse as well as transforming electric frequency.
A substation may contain transformers to change voltage, circuit breakers to cut off automatically the electric power, lightning arresters to divert the electric surge from the lightning to the ground, and so on.
In most cases, substations are located away from plain area where consumes a lot of electricity.
In such case for long distance electric power transmission, it is transformed to high voltage to save electricity loss.
Then, it is transformed to lower voltage in order of ultra-high voltage substations, primary substations, secondary substations, distribution substations, and finally to factories or houses.
A substation may contain transformers to change voltage, circuit breakers to cut off automatically the electric power, lightning arresters to divert the electric surge from the lightning to the ground, and so on.
In most cases, substations are located away from plain area where consumes a lot of electricity.
In such case for long distance electric power transmission, it is transformed to high voltage to save electricity loss.
Then, it is transformed to lower voltage in order of ultra-high voltage substations, primary substations, secondary substations, distribution substations, and finally to factories or houses.
Purpose and role of substations
1. Step up voltage to high for higher electricity transmission efficiency on long distance transmission.
2. Transform voltage to suit for each usage.
3. Connect or cut electricity lines according to necessity.
4. Distribute electric power to each places (ex. railway, factories, buildings, houses, etc.).
2. Transform voltage to suit for each usage.
3. Connect or cut electricity lines according to necessity.
4. Distribute electric power to each places (ex. railway, factories, buildings, houses, etc.).

Main equipment
The main equipment in a substation is described in more detail below.
- Transformers are the core equipment of substations, stepping up and down voltage. Large transformers use cooling oil to efficiently dissipate heat. The latest amorphous transformers and top-runner transformers contribute to improving energy efficiency.
- Circuit breakers play a vital role in interrupting current in the event of an accident or overload. They operate at high speed and have excellent arc extinguishing capabilities.
- On the other hand, disconnectors open and close the circuit when there is no load, and are used to ensure safety during maintenance and inspection.
- Switchgear controls the flow of electrical power. There are indoor switchgears and outdoor gas-insulated switchgears (GIS) to ensure reliability and safety.
- A busbar is a conductor that distributes power within a substation. It has multiple connection points and allows for efficient power transfer.
- A protective relay is a control device that detects abnormalities in the power system and issues operation commands to circuit breakers.
- Advances in digital technology have made it possible to provide advanced protective functions and remote monitoring.
- Instrument transformers measure voltage and current and provide information to control and protection systems.
- Surge arresters play an important role in protecting equipment from lightning strikes and switching surges.
By working together, these devices enable substations to maintain the stability and reliability of the power grid. The introduction of monitoring systems that utilize the latest IoT technology has enabled efficient operation and maintenance.
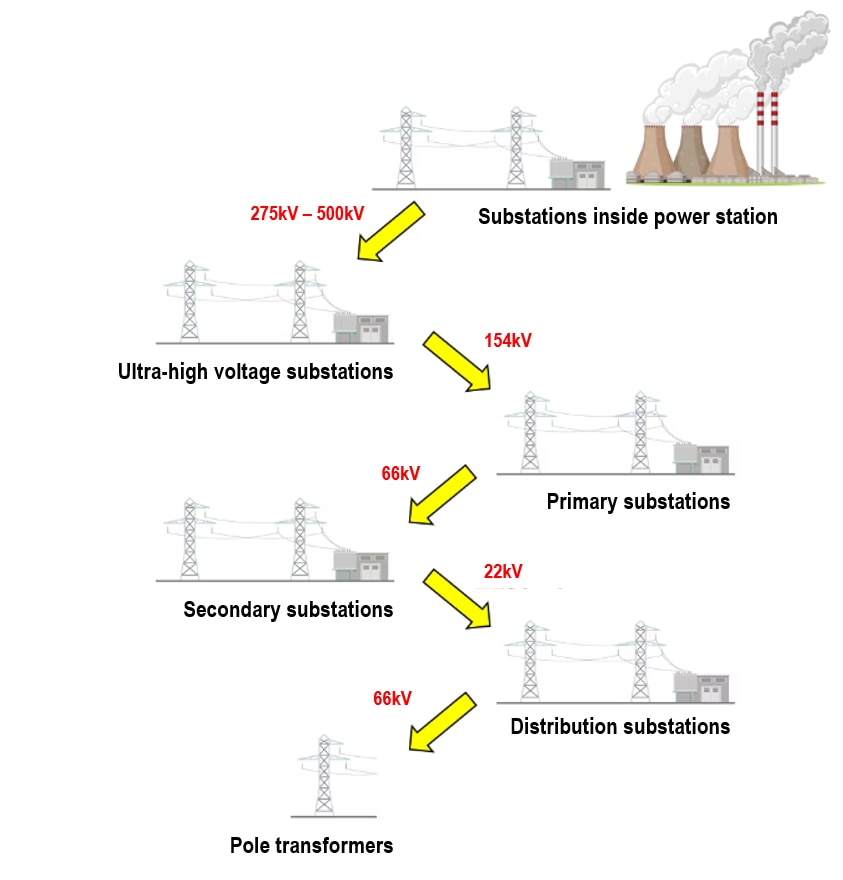
Flow of voltage transformation and power transmission
1. Substations inside (or alongside) the power station
* Step up voltage from the power station output (approx.20kV) to ultra-high voltage from 275kV to 500kV.
* Transmit electricity to Ultra-high voltage substations.
* Transmit electricity to Ultra-high voltage substations.
2. Ultra-high voltage substations
* Step down the ultra-high voltage transmitted from the substation in the power station to 154kV.
* Transmit the electricity to primary substations.
* Transmit the electricity to primary substations.
3. Primary substations
* Distribute 154kV electricity to railways or large factories.
* Step down the voltage to 66kV and transmit to secondary substations.
* Step down the voltage to 66kV and transmit to secondary substations.
4. Secondary substations
* Step down 66kV to 22kV.
* Distribute electricity to factories
* Transmit the electricity to distribution substations.
* Distribute electricity to factories
* Transmit the electricity to distribution substations.
5.Distribution substations
* Step down 22kV to 6600V
* Distribute electricity to factories or offices
* Transmit the electricity to
* Distribute electricity to factories or offices
* Transmit the electricity to
6. Pole transformers
* Step down 6600V to 200V or 100V
* Distribute electricity to houses or small offices
* Distribute electricity to houses or small offices
Importance of Environmental Monitoring in Substations
In addition to electrical protection and monitoring, environmental management plays a vital role in ensuring the stable operation of substations.
Dust and airborne particles can cause serious risks, such as:
- Reduced insulation performance, leading to arc discharge
- Blockage or reduced efficiency in cooling systems
- Intrusion into electrical equipment, causing malfunctions or shorter lifespan
- Increased risk of fire or even dust explosions in certain environments
To address these risks, more substations and power distribution facilities are now adopting dust sensors and particle counters for continuous monitoring.
Benefits of Using Dust Sensors and Particle Counters
- Early anomaly detection: Identify rising particle concentrations before faults occur
- Improved safety: Reduce risks of insulation failure or fire hazards
- Predictive maintenance: Enable efficient operation with real-time monitoring instead of relying only on periodic inspections
- IoT integration: Combine with remote monitoring systems to support automation and unmanned operation
Learn more about Dust Sensors and Particle Counters
Reference information
Please feel free to ask us if you have any questions
or you want our support. ⇩⇩⇩
Please feel free to contact us if you have any inquiries.
Click here to download documents.
© Matsushima Measure Tech Co., Ltd.



