Lithium-Ion Battery (Secondary battery) definition, structure, features, raw material reserves and loss reduction.
What is a lithium-ion battery (secondary battery)?

Lithium-ion batteries, a kind of secondary batteries, are essential rechargeable energy storage systems that power a wide range of modern technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles. They function through the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode, facilitated by a separator and electrolyte, with each component playing a vital role in ensuring efficient energy storage and release.
Secondary Battery Definition
Secondary batteries, also known as rechargeable batteries or accumulators, are energy storage devices that can be charged and discharged multiple times.
Unlike primary batteries, which are designed for single use, secondary batteries utilize reversible electrochemical reactions that allow them to be recharged by applying an external electrical current.
This ability to be recharged makes secondary batteries more cost-effective and environmentally friendly in the long run.
Key characteristics of secondary batteries include:
- High power density and discharge rates
- Good performance at low temperatures
- Ability to be used as both energy storage devices and portable power sources
- Applications in various fields, including electric vehicles, consumer electronics, renewable energy storage, and industrial backup power systems
- Common types include lithium-ion, lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, and nickel-metal hydride batteries
While secondary batteries offer numerous advantages, they may have lower energy density and higher initial costs compared to primary batteries.
Ongoing research focuses on improving their performance, safety, and sustainability to meet the growing demands of modern technology and energy systems.
Secondary Battery Types
Secondary batteries come in various types, each with distinct features and applications.
The most common types include:
- Lead-acid batteries: Known for their low cost and good high/low-temperature operation, they are widely used in cars, lawn mowers, and aircraft. However, they have low energy density and poor charge retention.
- Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries: Offer good physical durability and charge retention, but suffer from the "memory effect" and contain toxic cadmium. They are often used in aircraft and emergency power applications.
- Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries: Provide higher energy density than NiCd batteries and are more environmentally friendly. They are commonly used in consumer electronics and portable devices.
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries: Feature the highest energy density among secondary batteries, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles. They offer long cycle life and no memory effect, but are more expensive than lead-acid batteries.
Each type of secondary battery has its own advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications based on factors such as energy density, cost, cycle life, and environmental impact.
Advantages and disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Battery
Lithium-Ion Battery Benefits
Lithium-ion batteries offer several key advantages over other battery technologies, making them the preferred choice for many applications:
- High energy density: Li-ion batteries can store 3-4 times more energy than nickel-cadmium batteries of the same size, enabling longer device operation and smaller, lighter designs.
- Long cycle life: With proper care, Li-ion batteries can endure 2,000 or more charge-discharge cycles, lasting 8-10 years in many cases.
- Rapid charging: Li-ion batteries support fast charging, with some systems able to reach full capacity within an hour.
- Low self-discharge: When not in use, Li-ion batteries lose only 2-3% of their charge per month, maintaining power for longer periods.
- No memory effect: Unlike some other rechargeable batteries, Li-ion batteries do not need to be fully discharged before recharging, maintaining their full capacity.
These advantages make Li-ion batteries ideal for a wide range of applications, from portable electronics to electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
Lithium-Ion Battery Drawbacks
Lithium-ion batteries, despite their widespread use, have several notable disadvantages:
- Safety concerns: These batteries are prone to thermal runaway, potentially leading to fires or explosions, especially when damaged or improperly managed.
- Sensitivity to temperature extremes: Performance and lifespan can be significantly affected by exposure to very high or low temperatures.
- High production costs: The complex manufacturing process and materials used make lithium-ion batteries more expensive than some alternatives.
- Limited lifespan: Over time, lithium-ion batteries degrade, typically withstanding only 500-1000 charge cycles before capacity significantly decreases.
- Environmental impact: The extraction of lithium and other materials can damage ecosystems, contaminate water sources, and contribute to air pollution.
Additionally, lithium-ion batteries require protection circuits to prevent overcharging and deep discharging, adding complexity to their design and use.
The growing demand for these batteries also raises concerns about the long-term availability of key minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Structure and operation of Lithium-Ion Battery
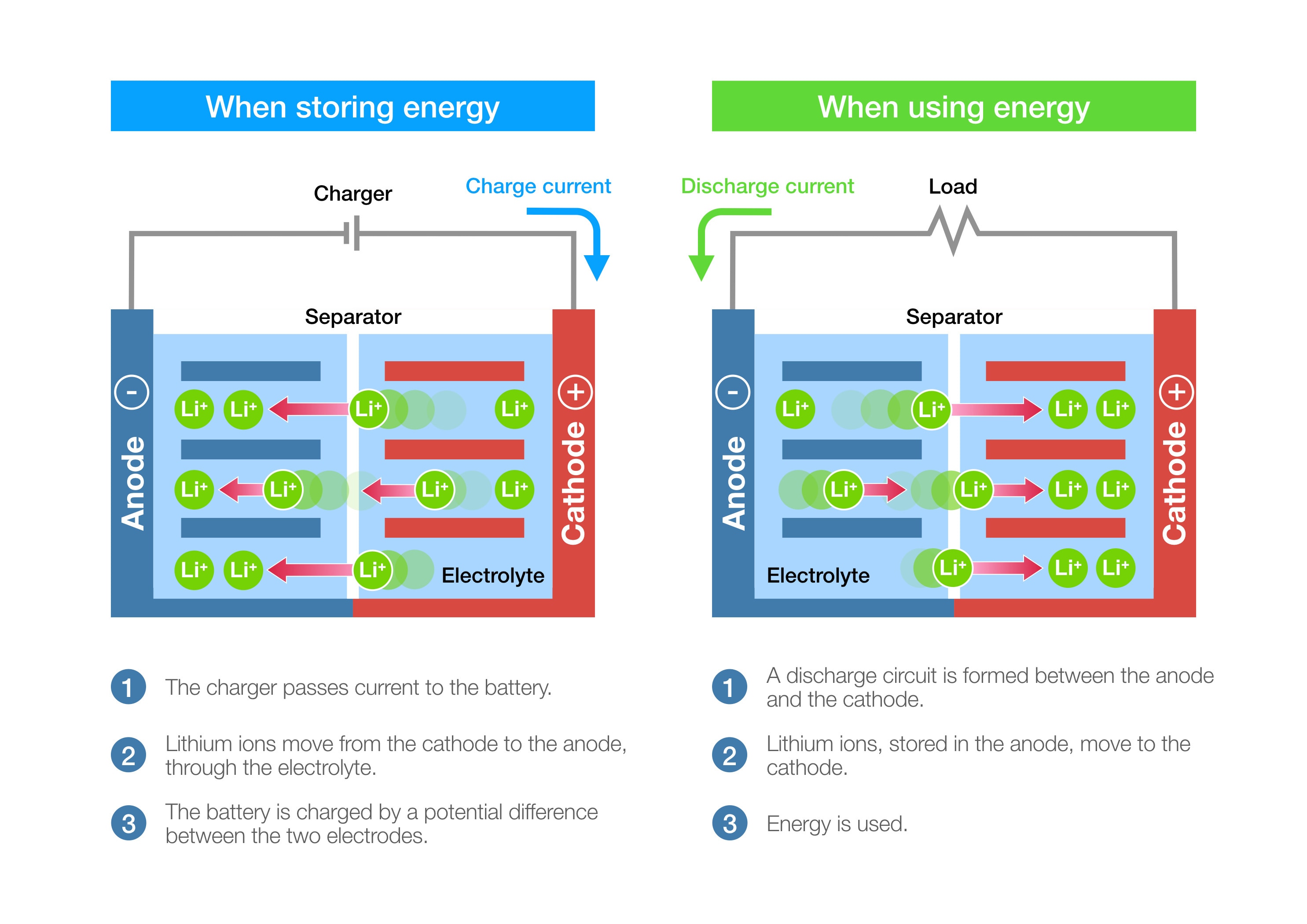
Lithium-ion batteries consist of four main components: a cathode, an anode, an electrolyte, and a separator.
The cathode is typically made of lithium metal oxide, while the anode is usually graphite.
The electrolyte, a lithium salt dissolved in organic solvents, facilitates ion movement between electrodes.
A microporous separator prevents direct contact between the electrodes while allowing ion flow.
The battery operates on the principle of reversible lithium intercalation.
During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte, while electrons flow through the external circuit.
This process stores energy in the battery. When discharging, the ions and electrons reverse direction, releasing energy to power connected devices.
This "rocking chair" mechanism of lithium ions moving back and forth between electrodes enables the battery's rechargeable nature and high energy efficiency.Anode and Cathode Functions
In a lithium-ion battery, the anode and cathode play crucial roles in the energy storage and release process. The anode, typically made of graphite, serves as the negative electrode during discharge, releasing lithium ions and electrons.
Conversely, the cathode, often composed of lithium-based compounds like lithium cobalt oxide, functions as the positive electrode, accepting these ions and electrons.
During charging, their roles reverse, with the anode accepting lithium ions and the cathode releasing them.
This reversible process of ion movement between electrodes, facilitated by the electrolyte, enables the battery to store and deliver electrical energy efficiently.
Separator's Role in Batteries
The separator is a critical component in lithium-ion batteries, serving as a permeable membrane between the anode and cathode.
Its primary functions include:
- Preventing physical contact between electrodes to avoid short circuits
- Allowing ionic transport through its porous structure to facilitate electrochemical reactions
- Providing mechanical support and maintaining proper electrode spacing
- Acting as an electrolyte reservoir to ensure uniform ion distribution
- Enhancing battery safety through thermal shutdown capabilities
Separators are typically made of microporous polymer films, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, designed to withstand the battery's chemical environment while maintaining structural integrity.
The separator's properties, including porosity, thickness, and thermal stability, directly impact battery performance, safety, and longevity.
Electrolyte Composition and Function
The electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries is a critical component that facilitates ion transport between electrodes. It typically consists of lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, with additives to enhance performance and safety.
The most common lithium salt used is lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), known for its excellent conductivity and stability.
Organic solvents often include a mixture of cyclic carbonates (like ethylene carbonate) and linear carbonates (such as dimethyl carbonate).
Key functions of the electrolyte include:
- Conducting lithium ions between electrodes during charge and discharge cycles
- Providing a medium for electrochemical reactions
- Forming a protective layer on electrode surfaces, known as the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI)
- Ensuring thermal and chemical stability within the battery
The composition and properties of the electrolyte significantly impact battery performance, including energy density, power output, and cycle life.
Ongoing research focuses on developing advanced electrolytes, such as solid-state and high-concentration electrolytes, to improve safety and performance in next-generation batteries.
Raw material and reserves of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Battery Raw Materials
Lithium-ion batteries rely on several key raw materials for their production, with the most critical components being:
- Lithium: Essential for the cathode and electrolyte, typically sourced from brine deposits or hard rock mines
- Graphite: Used in the anode, available in both synthetic and natural forms
- Cobalt: A crucial cathode material, primarily mined in the Democratic Republic of Congo
- Nickel: Increasingly important in newer cathode chemistries for improved energy density
- Manganese: Used in some cathode formulations to enhance stability and reduce costs
- Copper: Utilized for current collectors and wiring
The demand for these materials is expected to grow significantly as electric vehicle adoption increases. For instance, lithium demand is projected to rise 2.5 to 5 times by 2030, potentially reaching 240,000 to 450,000 tonnes annually.
While concerns about material scarcity exist, experts argue that there are sufficient resources to meet future demand, provided that exploration, production, and recycling efforts are scaled up accordingly.
Battery Material Reserves
Lithium-ion batteries rely on several key materials, with reserves varying significantly across the globe. Australia and Chile lead in lithium reserves, holding 9.3 million and 6.2 million tonnes respectively, valued at over $500 billion combined.
For nickel, a crucial component in advanced cathode chemistries, global identified resources total 300 million tonnes, with significant deposits in Indonesia, Australia, and Brazil.
Copper, essential for battery conductivity, has identified resources of 2.1 billion tonnes globally, with an additional 3.5 billion tonnes estimated in undiscovered deposits.
Cobalt reserves are highly concentrated, with the Democratic Republic of Congo dominating production.
Despite concerns about material scarcity, experts argue that there is no fundamental shortage of raw materials for lithium-ion batteries.
As demand increases, exploration and production of lower-quality ores are likely to expand, ensuring long-term supply availability for the growing energy storage and electric vehicle markets.
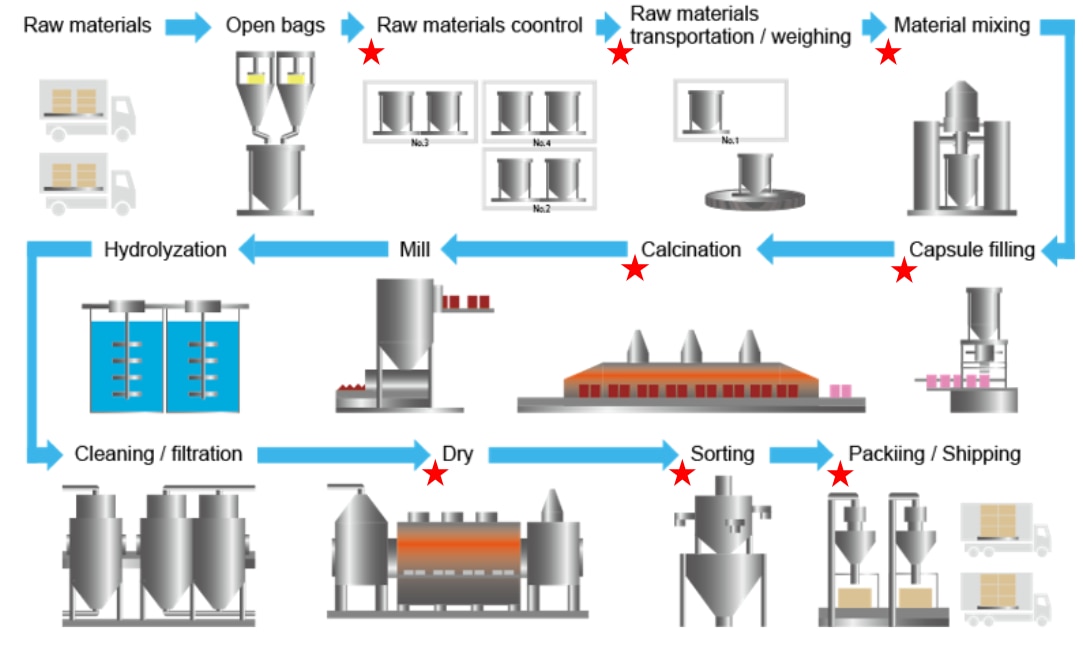
An example of successful raw material loss reduction
However, at one manufacturer's factory, more than 9 tons of raw materials were leaking uncollected every month from dust collectors at all factories due to installation errors and deterioration after filter cloths were replaced. This resulted in a loss of approximately 27 million yen per month for the company, and also led to air pollution problems.
Please feel free to ask us if you have any questions
or you want our support. ⇩⇩⇩
© Matsushima Measure Tech Co., Ltd.



