Environmental Monitors are essential tools for quantitatively evaluating various environmental elements such as air, water quality, soil and noise for measuring the quality of the environment.
These instruments accurately measure the concentration of harmful substances and noise levels and play an important role in environmental conservation, evaluation of health risks and confirmation of compliance with laws and regulations.
What are Environmental Monitors?
Environmental Monitors are important measurement instruments for quantitatively evaluating various elements in our living environment and monitoring the quality of the environment.
These instruments measure a wide range of environmental parameters including air, water quality, soil, noise and vibration as an essential role in environmental protection and health risk assessment.
Typical applications for Environmental Monitors include:
- Ensuring health and safety: Measuring the concentration of air pollutants to be used to assess the risk of respiratory diseases
- Environmental protection: Identifying and controlling pollution sources, preserving ecosystems
- Regulatory compliance: monitoring emissions at industrial facilities such as factories and power plants
- Data collection and research: Long-term trend analysis of environmental changes and construction of prediction models
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development: Environmental Impact Assessment for New Construction Projects
The data obtained by these devices is also an important source of information for formulating environmental policies and working towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Types of Environmental Monitors
Environmental Monitors are classified according to the object and application of the measurement as follows:
- Air Quality Monitors: Particulate Matter Monitor, Gas Concentration Meter (CO2, ozone, etc.), Anemometer, Wind Vane, Thermometer, Hygrometer
- Water Quality Monitors: pH meter, Dissolved Oxygen Meter, Turbidity Meter, Electrical Conductivity Meter
- Soil Monitors: Soil Moisture Sensor, Soil pH Meter, Soil Hardness Meter
- Noise Monitors: Sound Level Meter, Low Frequency Sound Pressure Level Meter
- Vibration Monitors: Vibration Level Meters, Seismometers
These measuring instruments are used for various purposes such as environmental protection, compliance with laws and regulations for ensuring health and safety. For example, Air Quality Monitors are used for monitoring air quality in cities and managing exhaust gases from factories and Water Quality Monitors are used for evaluating the water quality of rivers and lakes.
When selecting an environmental monitoring instrument, it is important to consider measurement accuracy, usability and maintenability.
Overview of Air Quality Monitors
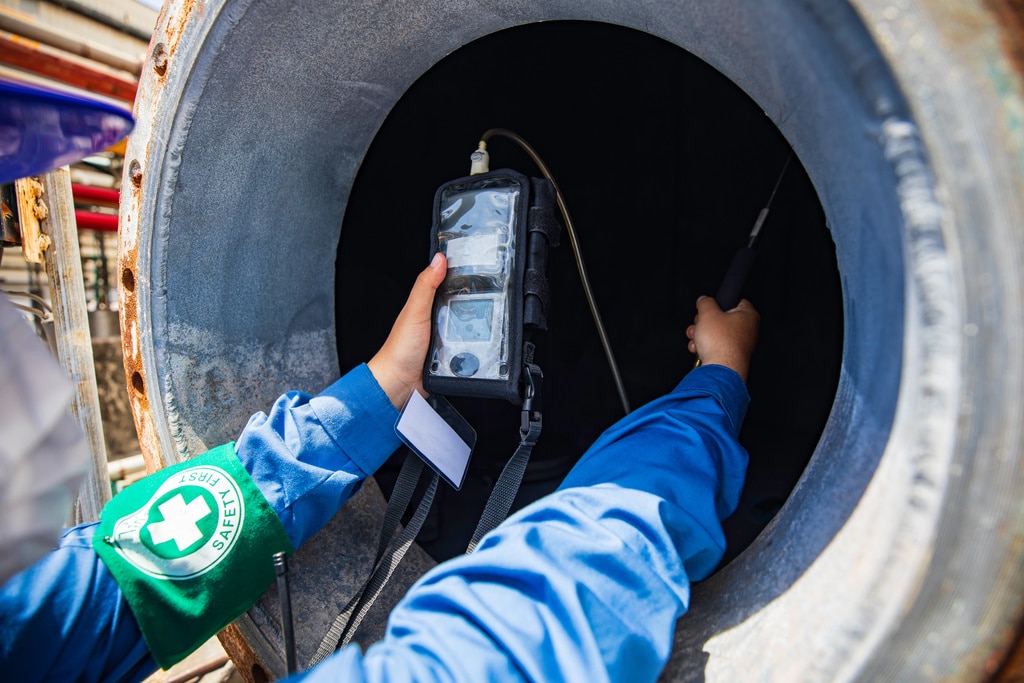

Air Quality Monitors are important devices for measuring the state and composition of the atmosphere.
The main types include:
- Particulate Matter Monitors: There are light scattering, beta ray absorption, filter vibration and piezoelectric balance methods which measure the concentration of fine particles in the air. The light scattering method allows for real-time measurement while the beta ray absorption method is suitable for continuous measurement.
- Gas Concentration Meter: Measures the concentration of specific gas components such as nitrogen oxides with high sensitivity and speed using chemiluminescence and absorption photometry.
- Total Hydrocarbon (THC) Concentration Measuring Devices are also included in this category.
- Meteorological Observation Equipment: Anemometers, Wind Vanes, Thermometers, etc. which use the principles of rotation, sound waves, temperature sensors, etc. These play an important role in weather forecasting, climate research and disaster prevention.
These devices are used for a variety of purposes including environmental monitoring, health impact assessment and regulatory compliance.
The balance between measurement accuracy and usability is important and it is necessary to select the appropriate device depending on the purpose of use.
Overview of Water Quality Monitors
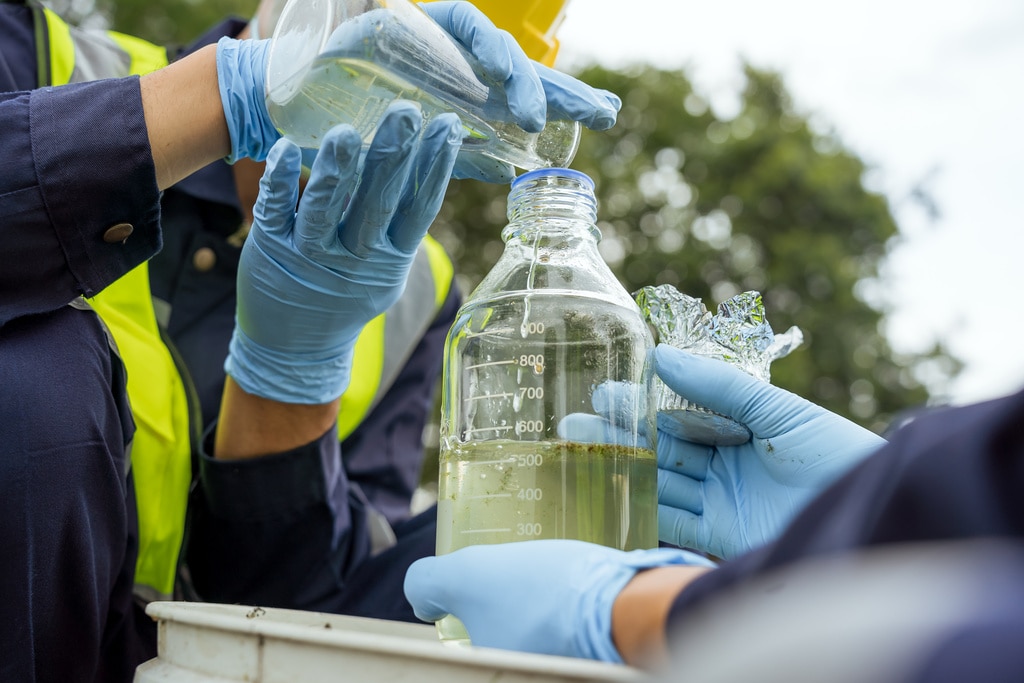

Water Quality Monitors are important tools for evaluating the chemical, physical and biological properties of water.
The main types include:
- pH meter: Measures the acidity of an aqueous solution using the glass electrode method. The measurement range is usually 2 to 12 pH with an accuracy of about ±0.2 pH.
- Dissolved Oxygen Meter: Measures the amount of dissolved oxygen in water using a polarographic or galvanic electrode method. The measurement range is 0 to 20 mg/L and the accuracy is about ±0.4 mg/L.
- Electrical Conductivity Meter: Measures the electrical conductivity of water using a two-electrode or four-electrode type to estimate the ion concentration in the water. The four-electrode type has the advantage of being less susceptible to dirt and polarization.
- Turbidity Meter: Measures the turbidity of water using the transmitted light method. The measurement range is about 0 to 2/4 degrees.
These instruments are used for a variety of purposes including early detection of water pollution, environmental protection, water resource management and maintaining public health. In many cases, multiple measuring instruments are used in combination to monitor water quality 24 hours a day.
Overview of Soil Monitors
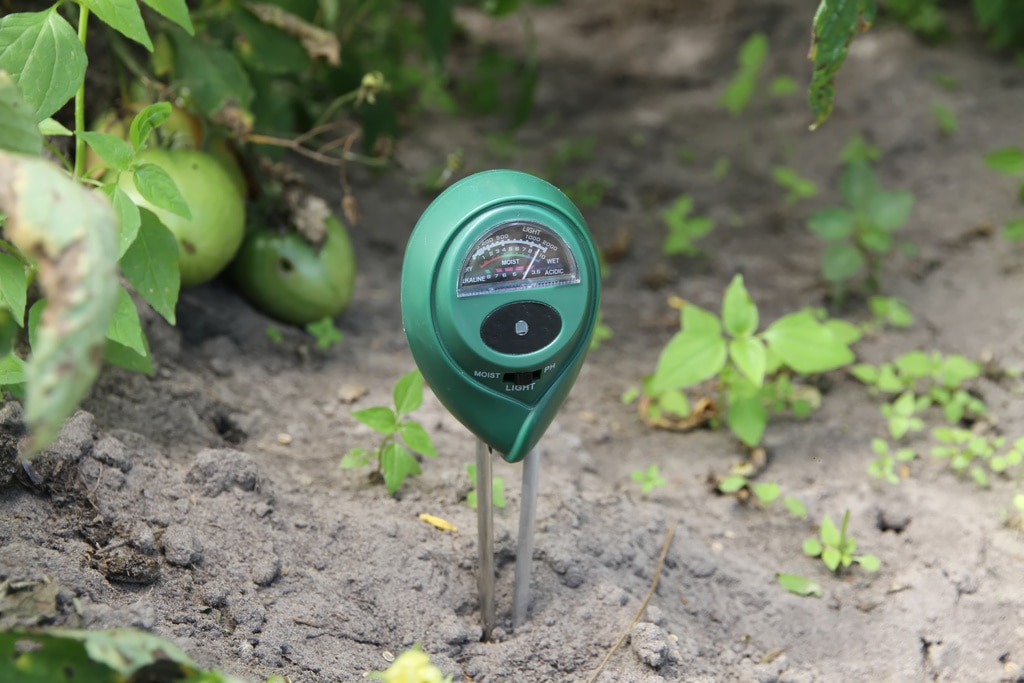

Soil Monitors play an important role in the agricultural and environmental science fields to evaluate soil properties.
The main types include:
- Soil Moisture Sensor: There are TDR (Time Domain Reflectometry) and TDT (Time Domain Transmission) methods which measure the soil's dielectric constant to determine the moisture content.
- The TDR method uses straight electrodes while the TDT method uses loop electrodes.
- Soil pH Meter: Inserts directly into soil to measure acidity. The measurement range is usually around pH 4 to 7. If the soil is dry, water should be sprinkled before measuring.
- Soil Hardness Tester: Inserts a cone into the soil and measures the hardness from the degree of compression of the spring.
- Soil Salinity Meter: Measures the electrical conductivity of the soil to estimate the salinity concentration.
These instruments are used for a variety of purposes including optimizing the growing environment for crops and evaluating soil contamination. In many cases, multiple instruments are used in combination to perform a comprehensive soil evaluation.
Overview of Noise Monitors
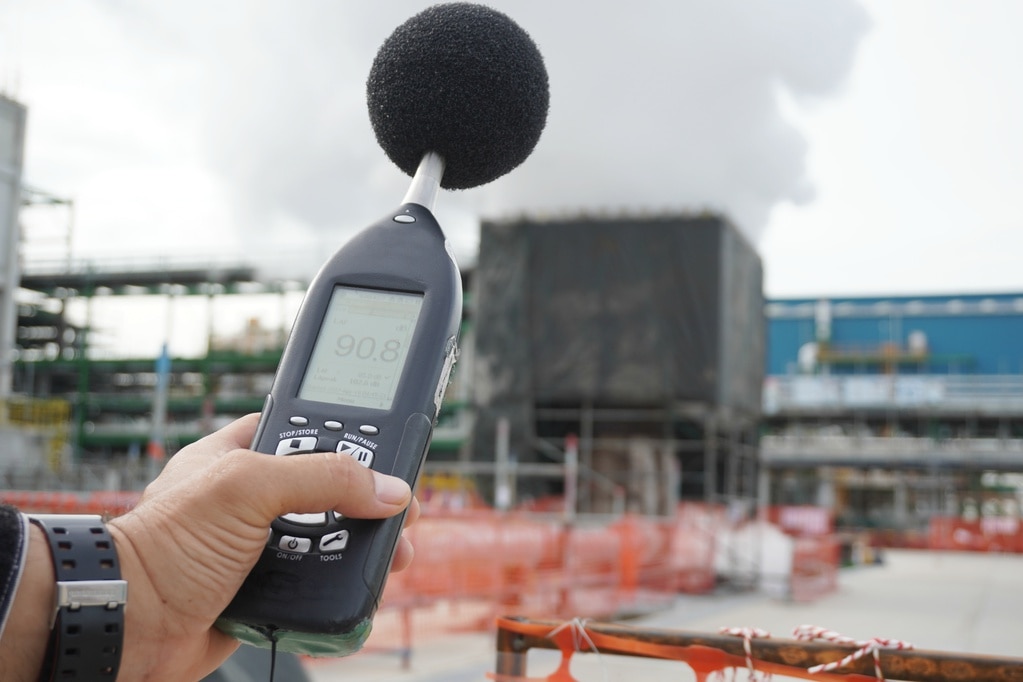

There are two main types of Noise Monitors: ordinary Sound Level Meters and precision Sound Level Meters. Ordinary Sound Level Meters are suitable for general environmental noise measurements and can measure in the frequency range of 20Hz to 8000Hz.
On the other hand, precision Sound Level Meters are more accurate and cover a wider frequency range from 20Hz to 12500Hz and are used in research and evaluation of acoustic products.
The basic mechanics of these Sound Level Meters are as follows:
- Microphone converts sound into an electrical signal
- Amplify the signal with an amplifier
- Frequency weighting processing is performed to adjust to the characteristics of human hearing.
- Analysis results displayed in decibels (dB)
High-performance Sound Level Meters are equipped with logging and low-frequency sound measurement functions enabling long-term continuous measurement and detailed analysis.
These devices are used for a variety of purposes including environmental assessments, industrial noise monitoring and noise management at construction sites.
Overview of Vibration Monitors
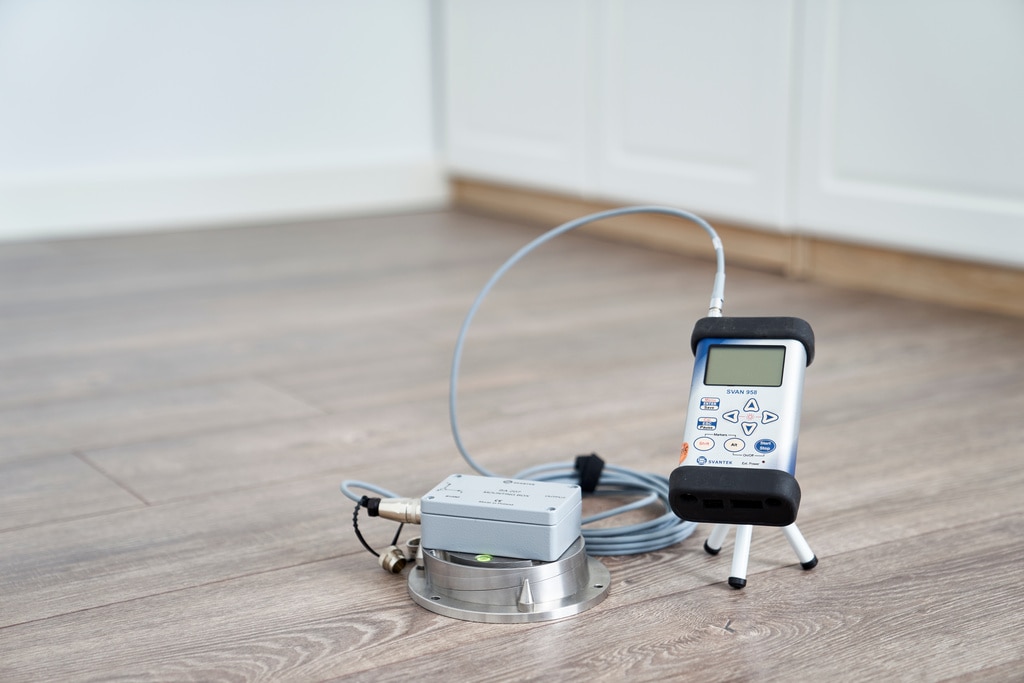

Vibration Monitors are important instruments for detecting and quantifying vibrations in structures and machines.
The main types include:
- Piezoelectric Vibrometer: Uses a piezoelectric element to generate an electric charge proportional to the force of vibration. High sensitivity and wide frequency range measurement possible.
- Frequency Change Type Vibrometer: Converts the oscillation frequency change of the acceleration sensor element into a digital value. It is small and inexpensive.
- Optical Vibrometer: Uses laser light to measure vibrations without contact. Suitable for measuring hot objects or objects at long distances.
The basic principle of a vibration measuring instrument is to convert vibration into an electrical signal using a weight and a spring. The measured vibration is expressed as a physical quantity such as acceleration, velocity and displacement.
These devices are used in a wide range of fields including factory facility maintenance, earthquake resistance evaluation of buildings and environmental vibration measurement.
Reference Articles
Please feel free to ask us if you have any questions
or you want our support. ⇩⇩⇩
© Matsushima Measure Tech Co., Ltd.



