Industrial Bag Filter
What is a bag filter?
Reference Article:
Structure and Working Principle
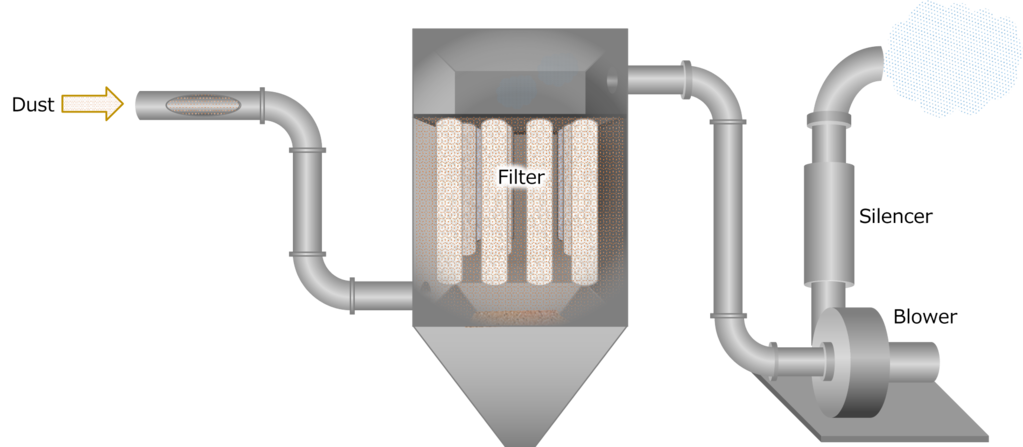
Filter materials include fibers such as polyester, heat-resistant nylon and glass fibers and are to be selected depending on the properties of the gas and dust.
Dust collection capacity may decrease if a large amount of dust adheres to the surface of the filter.
Then periodical backwashing (pulse jet) is achieved to remove the adhered dust.
Brushed off dust is stored in a dust box and is periodically discharged.
Maintenance
In recent years, dust monitors have been increasingly installed on the secondary side (gas discharge side) of bag filters to constantly monitor the dust leak amount. In fact, continuous monitoring the amount of dust leakage (dust concentration) with a dust monitor can help optimized timing of replacing filter cloth and reduce maintenance costs.

Importance of leakage monitoring
Problems caused by dust leakage
For example, dust will leak out if a filter is broken, and the leaked dust may adhere to the inside of the blower to cause corrosion. Due to this corrosion, loads are given on various parts of the blower, and in some cases, it may even stop. It is important to understand possible problems and take countermeasures before such a situation occurs.
Countermeasure: Monitoring dust concentration
Productivity improvement by predictive maintenance with Dust Monitor
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a kind of maintenance strategy focusing on monitoring actual situation of facility and predicting future failure risk.
It detects the sign of abnormality of future failure by achieving real time monitoring of machine situation with sensors or data analyzing tools.
It is possible to take countermeasures before failure happens and prevent unexpected sudden facility stop and then maximize the lifetime and occupation rate of facility.
Successful References
Types of Filter Bags for Industrial Dust Collectors
Industrial dust collectors rely on filter bags to capture and contain airborne dust and particulates, ensuring cleaner air and compliance with environmental standards. The choice of filter bag depends on the application, dust characteristics, operating temperature, and chemical environment. Below is an overview of the main types of filter bags used in industrial dust collectors, their materials, and typical applications.
Filter Bag Materials
- Polyester: Widely used due to its excellent resistance to chemicals, dry heat degradation, and abrasion. Suitable for operation up to 135°C and commonly used in industries such as cement, food processing, and general manufacturing.
- Polypropylene: Good for lower temperature applications (up to 80°C) and offers excellent resistance to acids and alkalis. Often used in chemical and food industries.
- Fiberglass: Suitable for high-temperature applications (up to 260°C) and offers good resistance to acids and water. Common in steel, foundry, and power generation industries.
- PTFE (Teflon): Exceptional chemical and temperature resistance (up to 260°C). Ideal for aggressive chemical environments and industries producing corrosive dust, though more expensive.
- PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide): Handles temperatures up to 190°C, resistant to acids and alkalis, and used in coal-fired boilers, incinerators, and chemical plants.
- Nomex (Aramid): Withstands temperatures up to 205°C, good for asphalt plants and applications with high heat and abrasion.
- P84 (Polyimide): Excellent for high-temperature and high-emission environments, with stable performance up to 240°C.
- Cotton Woven: Used in shaker-type collectors for applications with lower temperatures (up to 82°C), such as woodworking and cement.
- Nylon: Good for highly abrasive dust and moderate temperatures (up to 77°C), with good resistance to alkalis.
Filter Bag Shapes and Construction
- Round Bag Filters: The most common shape, used in standard baghouse systems.
- Flat Bag Filters: Provide a larger filtration area per unit volume, used where space or filtration efficiency is a concern.
- Pleated Filter Bags: Offer increased surface area, improving dust-holding capacity and filtration efficiency. Suitable for fine dust and energy-efficient operations.
- Two-Layer and Diamond Filters: Specialized designs to increase filtration area and efficiency for specific applications.
Types of Dust Collector Systems and Corresponding Filter Bags
| Collector Type | Typical Filter Bag Material | Application Example |
| Pulse Jet | Polyester, PTFE, PPS, Fiberglass, Nomex | Cement, steel, chemical, power plants |
| Shaker Type | Cotton, Polyester, Polypropylene | Woodworking, cement, general manufacturing |
| Reverse Air | Polyester, Fiberglass, Nomex | Foundries, steel, large-scale baghouses |
Key Selection Criteria
- Operating Temperature: Choose a material that can withstand the system’s maximum temperature.
- Chemical Resistance: Match the filter media to the chemical composition of the dust.
- Dust Characteristics: Consider abrasiveness, particle size, and moisture content.
- Filtration Efficiency: Select the appropriate micron rating and surface treatment for the desired air quality.
Summary Table: Common Filter Bag Materials and Properties
| Material | Max Temp (°C) | Chemical Resistance | Typical Use Cases |
| Polyester | 135 | Good |
Cement, food, general industry |
| Polypropylene | 80 | Excellent (acid/alkali) | Chemical, food |
| Fiberglass | 260 | Good (acid/water) | Power, steel, foundry |
| PTFE | 260 | Excellent | Chemical, glass, high-corrosive |
| PPS | 190 | Good | Incinerators, coal-fired plants |
| Nomex | 205 | Moderate | Asphalt, high-temp industrial |
| P84 | 240 | Good | High emission/high temp |
| Cotton | 82 | Poor | Woodworking, low-temp applications |
| Nylon | 77 | Good (alkali) | Abrasive dust, minerals |
Conclusion
Selecting the right filter bag for an industrial dust collector involves considering the dust type, temperature, chemical environment, and system design. Polyester and fiberglass are among the most commonly used materials, but specialized options like PTFE, PPS, and Nomex are chosen for harsh or high-temperature environments. Filter bag shape and construction—such as pleated or flat designs—can further optimize performance for specific industrial needs.
Reference Products
Please feel free to ask us if you have any questions
or you want our support. ⇩⇩⇩
© Matsushima Measure Tech Co., Ltd.



